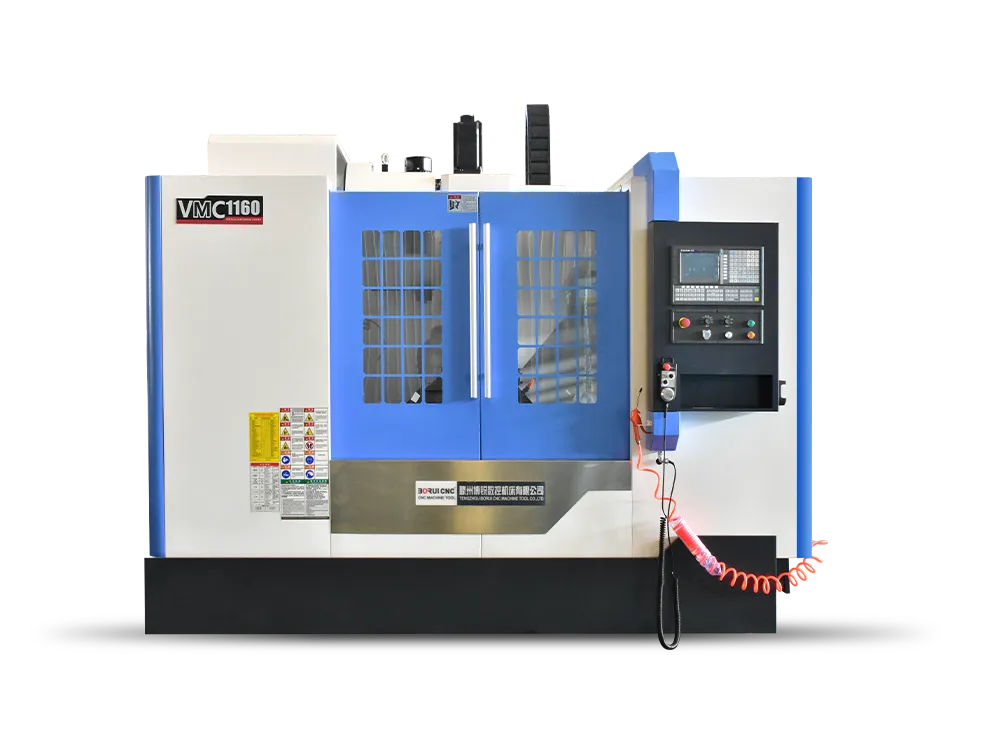
Technological advancement has led to more accurate and precise machines with automated controls. Modern manufacturing has made CNC milling machines the new norm. These machines enable the precise cutting, drilling, and forming of materials, which can only be accomplished with the aid of computer controls. They primarily serve the purpose of processing raw materials (such…
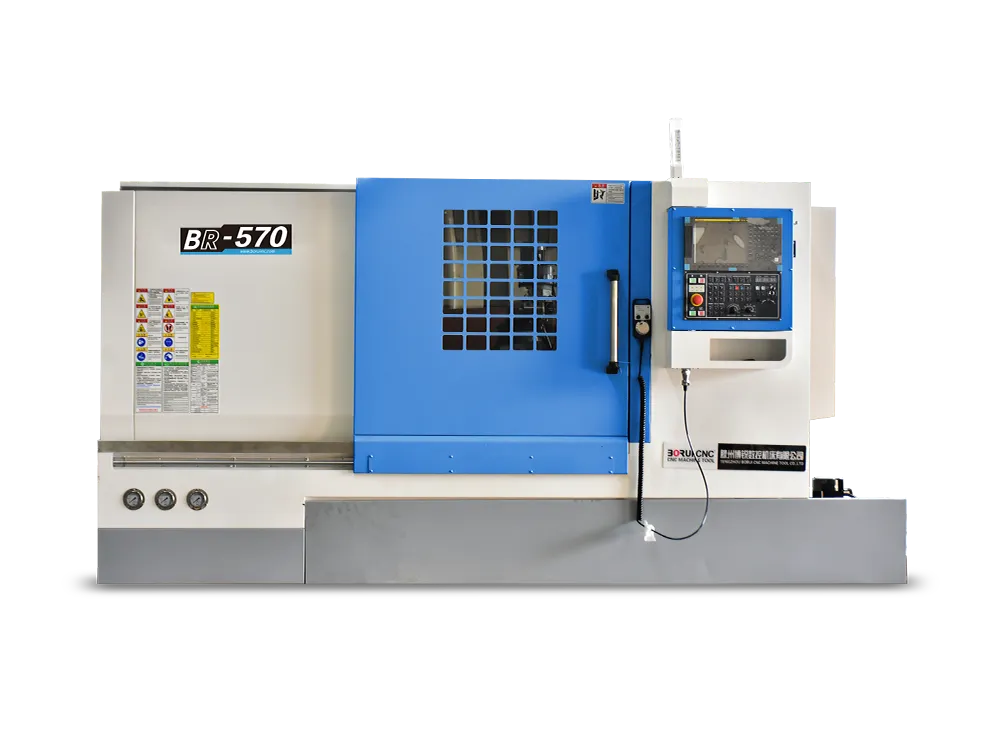
The lathe is not new! The use of the lathe dates back centuries in ancient civilizations. It was when the work was fully manual. Then, with the Industrial Revolution, it was powered by steam engines and water wheels. Advancing further, we now have CNC lathe machines that are precise and accurate shaping tools to create…
Lathes are incredible tools with a centuries-long history. A lathe machine works simply by rotating the workpiece around its axis to produce symmetrical objects. They are used to cut, shape, thread, drill, and polish the various materials. Its marvels have spread across multiple industries in the manufacturing field, offering unique benefits. From the challenging aerospace…
A 5-axis CNC machine is an incredible tool for complex manufacturing needs. On a 5-axis CNC machine, the cutting tool can move along X, Y, and Z axes, plus two rotating axes that operate simultaneously. It can cut workpieces from almost any direction. These machines handle intricate designs with tight tolerances. That’s why they are…
Not many tools can claim a title as bold as “mother of all machine tools,” yet the lathe machine earns it. Its earliest form is over 3,000 years ago—around 1300 BCE—in ancient Egypt. It gave artisans something new back then: the ability to rotate and shape materials evenly instead of carving by hand. That simple…
Are you looking for cutting-edge CNC machines to improve your metalworking skills? Join us at the 25th International Exhibition of Metalworking Equipment, Instruments and Tools, where Tengzhou Borui CNC Machine Tool Co., Ltd. will demonstrate our strength with two popular CNC machines. METALLOOBRABOTKA 2025, taking place from May 26 to 29, 2025, at Expocentre Fairgrounds,…
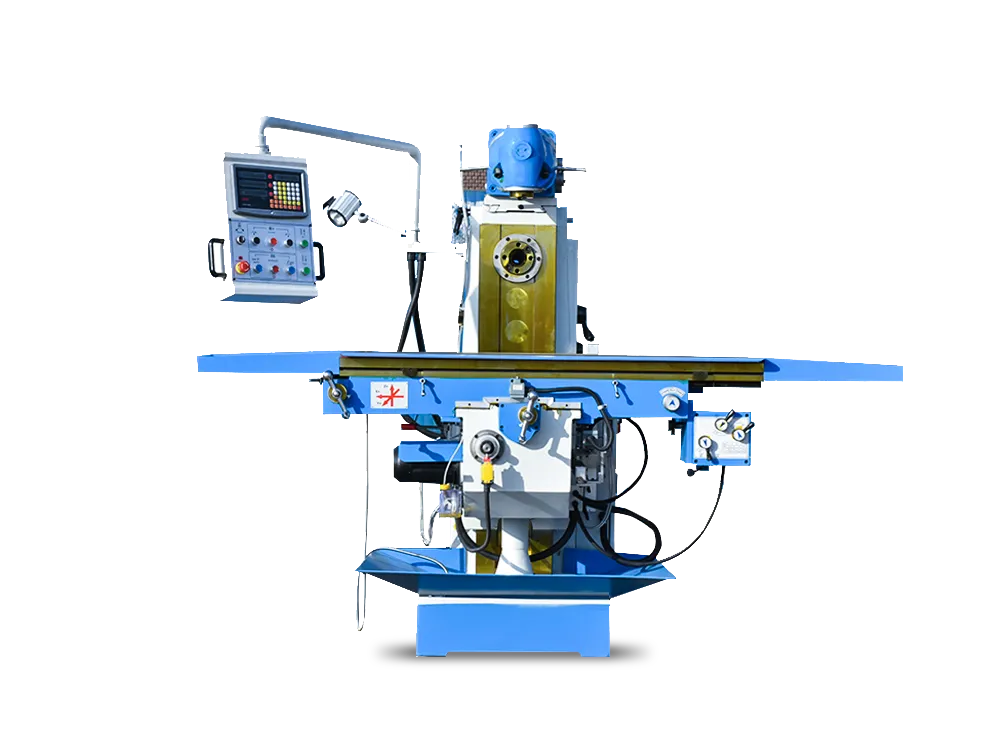
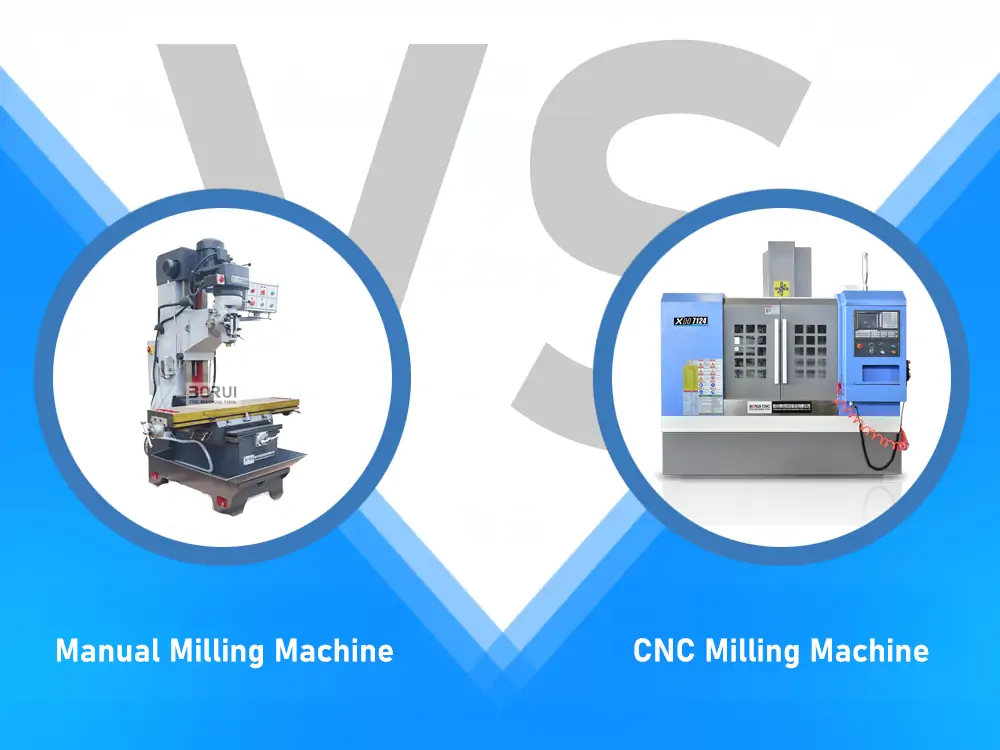
Long before, manual milling machines were the backbone of every machine shop. Machinists relied on their skill and steady hands to shape metal into useful parts. Every move depended on the machinist’s skill and their deep understanding of tools and materials. Today, CNC milling machines have changed the game. Now, these machines make parts fast…
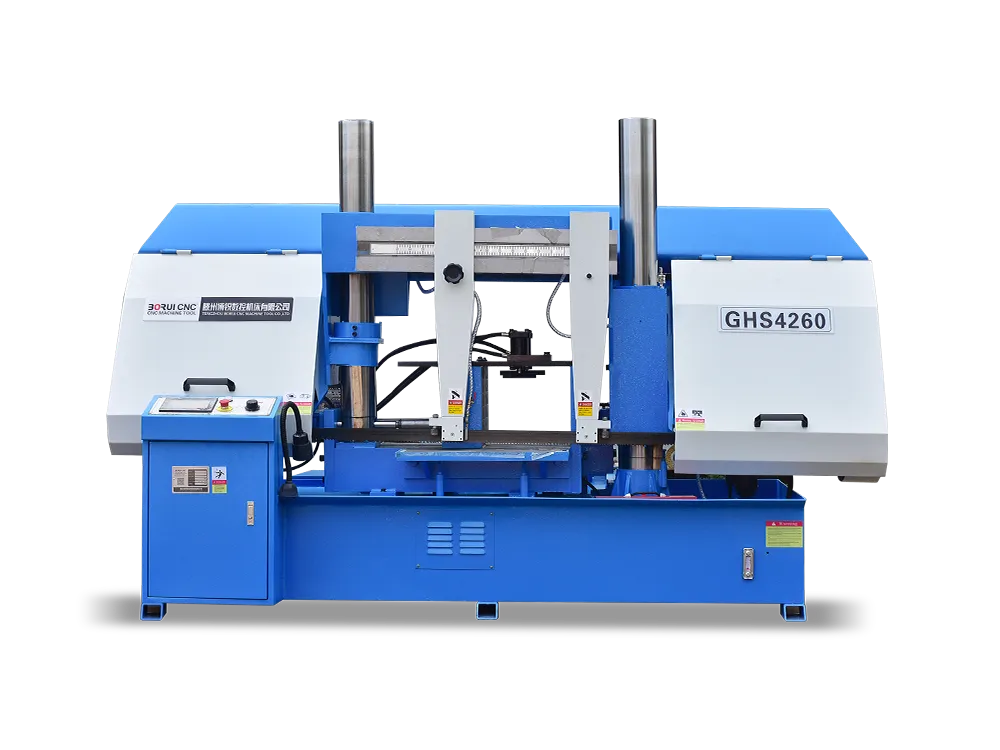
Multiple workshops rely on band saw machines as essential operational tools. In 2025, a number of companies will manufacture these precise cutting machines. These devices use advanced technology to perform precise cuts on wood, metal, and other materials. They perform essential operations in the automotive, aerospace, and construction industries. In this guide, we will walk…
Introduction Stepping into the world of CNC machining can be both exciting and overwhelming. The right machine benefits beginners who aim to turn their ideas into physical reality. Computer Numerical Control technology completely transformed manufacturing practices. Its precision and consistent performance during part creation establish a new standard. Using CNC machining equipment allows beginners to…
Tengzhou Borui CNC Machine Tool Co., Ltd. is proud to join the 19th China International Machine Tool Exhibition 2025, a top event for the global manufacturing sector. This exhibition will occur from April 21 to 26, 2025, at the China International Exhibition Center (Shunyi Pavilion) in Beijing. Visit us at Booth A2-763 to see our…